Payroll And Taxes
With the population of 1.2billion people, India is the seventh largest country in
the
world with an average growth rate of 5.8% per year. Recently India has achieved
remarkable growth in pharmaceuticals, petroleum, software and biotechnology
industries.
India’s huge population and economic growth also make the country a very attractive
market for foreign investors and products. In the year 2011, it was ranked as the
10th
largest importer and the 19th largest exporter in the world.
The rapid growth in industrialization gives a high rise in employment rate and
different
kind of taxes. Understanding of these taxes is very important for every employee and
employer to avoid any complications. This article will give you a clear idea about
the
calculation of payroll and taxes in India.
Payroll Options in India
There are plenty of options available regarding the development and application of
payroll system.
-
Fully Outsourced Payroll Department
Foreign companies who are operating or want to extend their business boundary to India, could face a lot of difficulties in understanding and comply with tax rules applicable in India. To avoid all these difficulties, foreign companies can outsource their payroll to third party companies, who will pay on their behalf.
-
Internal Payroll
Foreign or local companies, which are registered in any available business form, and make their own internal payroll system will have to follow the local laws at the time of salary disbursement.
Calculation of Payroll
Payroll is generally the list of employees, employed in any business or non-business
entity. Payroll also refers to the total amount of money the employer pays to the
employee against the services provided.
The pay slip of the employee should consist of all the benefits allowed to the
employee
like basic pay, variable pay, and allowances. The employer is liable to deduct all
the
necessary taxes and other deductions according to the law and regulations. So the
net
pay would be termed in mathematical form as
Net pay = Gross Pay – All necessary deductions
While,
Gross pay = All type of basic pay + allowances + any other special benefit
Necessary Deductions= All basic type deduction – deductions applicable under law
+ any other special deduction.
Deductions from payroll are normally TDS, PF, ESI, and PT, etc.
- TDS can be calculated as (Basic salary + allowance – deductions) *12 – IT deductions
- PF or Provident fund is 12% of the basic salary of 15% whichever is lower
- While ESI amounted to 1.75% of 21000 or gross pay, whichever is lower.
Salary structure for 2018-2019 with all the tax details are as follows:
| Element | Taxation Treatment | PF applicable | Part of Gratuity | Minimum Amount |
| Basic Salary | Fully taxable | Yes | Yes | As per Minimum wage |
| DA | Fully taxable | Yes | Yes | As per Minimum wage |
| Medical & Convenience | Fully taxable | No | No | None |
| HRA | Exempt up to the following 3 conditions 1.Actual HRA 2.50% of basic salary+40% of Basic if DA is metro+ DA if non metro 3. 10% of basic rent |
No | No | Depends on the state |
| LTA | Actual expense | No | No | None |
| Education Allowance | For 2 children Rs.100 | No | No | None |
| Car Maintenance | 2400 per month | No | No | None |
| Driver Salary | Driver salary up to 900 | No | No | None |
| Special Allowance | Fully Taxable | No | No | None |
Details of Deductions and their calculation:
| Name of Deductions | Calculation | Application |
| PF (Provident Fund) | 12% of basic salary + DA + Any special allowance | Companies with 20 or more employees. Apply on all the employees whose basic + DA + Special is less than 15,000 INR per month. |
| ESIC | Employer contribution = 4.75% Employee contribution = 1.75% |
Companies with 20 or more employees, whose salary per month is less than 21,000. |
| Professional Tax | Every state have their own rules | All employees where this is applicable |
| labor Welfare Fund | Every state have their own rules | All employees where this is applicable |
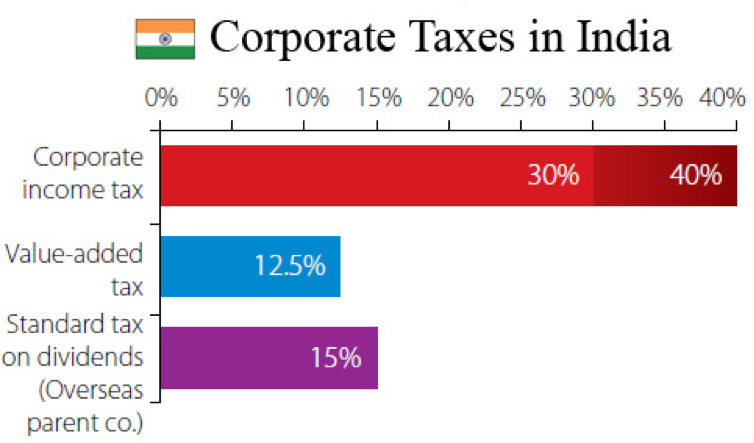
In addition to all these taxes, there are another type of tax known as income tax is also applicable on the individuals who’s income falls in that category is called income tax.