Balance Sheet Format
Balance sheet is one of the financial statements that a company prepares annually
along with the income statement, cash flow statement and statement of changes in
equity. Balance sheet, which is also known as the statement of financial position,
shows the assets, liabilities and equity of a company at a particular date. Usually,
it is prepared at the end of an accounting period but is often prepared quarterly
or semi-annually as well.
Balance sheets are used by creditors, investors, and business owners to analyze
the business’s financial performance or financial analysis. Creditors and investors
use the balance sheet to understand how the company is financing its assets and how
efficiently is it using its resources.
Balance sheet shows us the accounting equation i.e. the sum of the assets equals the
liabilities and equity as shown below:
Total Assets = Total liabilities + Equity
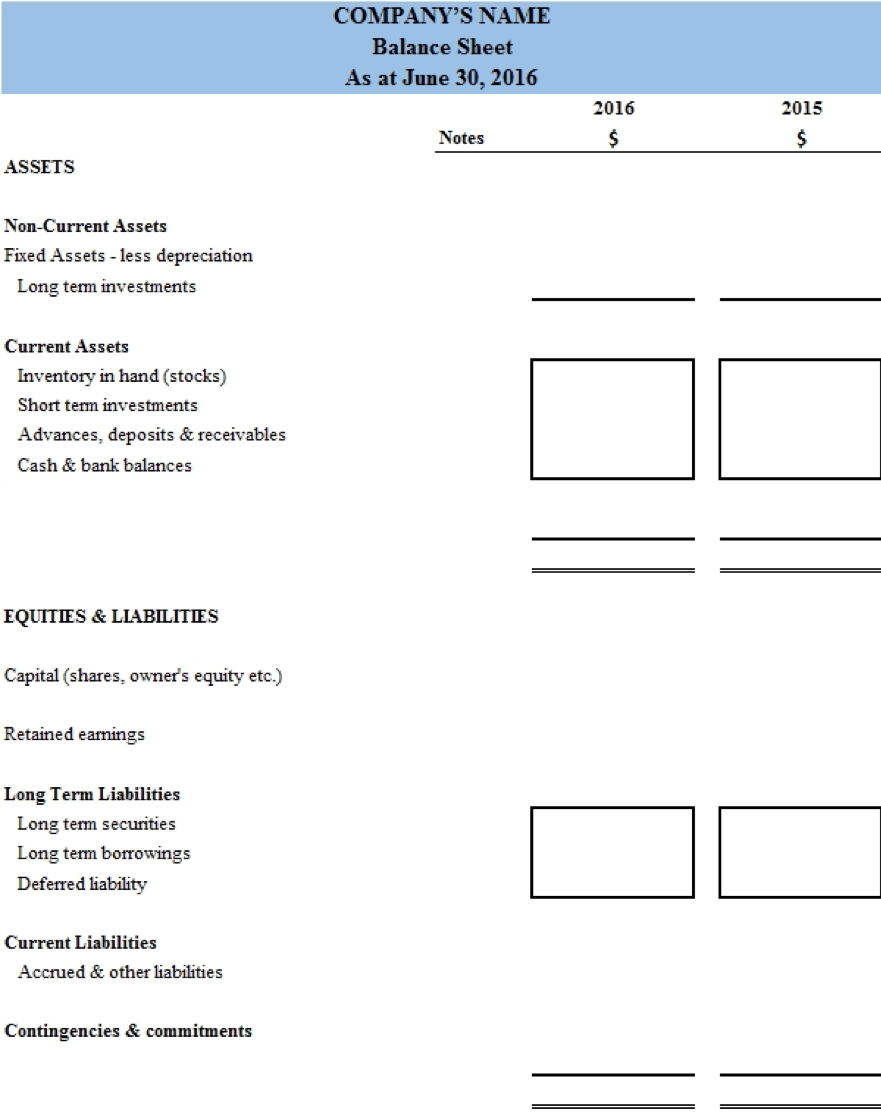
The first line item of a balance sheet is “asset”. Assets are resources owned by a
company
that are used to generate future economic benefits for the company. They are usually
recorded at their cost at the time of acquisition and can be divided into two
categories
- intangible and tangible. Tangible assets are the assets that have a physical form
or
are physically present with the company. On the other hand, intangible assets are
resources owned by the company that have no physical form for example: patents,
trademarks, goodwill of the business, copyrights and licenses.
Tangible assets are further categorized into two categories:
- Current assets:
These are assets which are liquid or can be converted into a liquid form and consumed within an accounting period, which is usually one year. Current assets reflect liquidity of a company which in other words can be defined as the ability of a company to convert assets into cash. Too much liquidity and too less liquidity, can be problematic for a company. A perfect ratio has to be found in order to meet all the objectives of the business. Current assets' examples include cash and bank, debtors, prepaid expenses, inventory etc. -
Fixed or non-current assets:
Fixed assets are to be used over a longer period of time which is more than a year. These are huge investments usually that are used to manufacture goods or services for the company. Examples include factory, office building, plant and machinery and furniture. As per the IAS, these are reported on the balance sheet at their book values i.e. Cost less depreciation.
The other half of balance sheet is the sum of equity and liabilities.
Shareholder’s equity includes the share capital, retained earnings and reserves.
Share
capital is the common stock and preferred stock of the company i.e. the funds
collected
by issuance of shares. Similarly, retained earnings are the leftover profit after
distribution of dividends. Lastly, reserves are the surpluses the company has
accumulated
and can be used in times of reoccurring losses or when payments have to be
made.
Lastly, Liability is the amount of money a business owes to other parties. In other
words,
it is the obligations the business has to fulfill within a given period of time. It
can be
categorized into two types as well:
- The current liabilities have to be met within one year or one accounting period. Current liabilities include interest payments, prepaid payments made to the company, notes payables, accounts payables and other payables. A high current liabilities balance may indicate liquidity problems and difficulties in meeting payment deadlines.
- Long- term liabilities, on the other hand, are paid back over a time period of more than a year. This balance signifies that the company is investing in the business and has a long term goal in mind. It includes bank loans, bonds payable etc.
Conclusion:
It is a statutory compulsion for every business to prepare their financial
statements
as per the applicable reporting framework i.e. IFRS. In order to meet the regulatory
requirements, it is crucial for the business management to know the meanings of each
item reported on the balance sheet as well as prepare the financial statements in
the
specified format.